We’ve added this new abstract to our Publications Abstracts resource page.
Hyperprolactinemia due to spontaneous intracranial hypotension
Schievink WI, Nuño M, Rozen TD, Maya MM, Mamelak AN, Carmichael J, Bonert VS
J Neurosurg. 2014 Nov 7:1-6. [Epub ahead of print]
Abstract
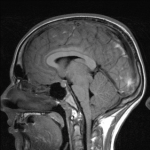
OBJECT: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension is an increasingly recognized cause of headaches. Pituitary enlargement and brain sagging are common findings on MRI in patients with this disorder. The authors therefore investigated pituitary function in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension.
METHODS: Pituitary hormones were measured in a group of 42 consecutive patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. For patients with hyperprolactinemia, prolactin levels also were measured following treatment. Magnetic resonance imaging was performed prior to and following treatment.
RESULTS: The study group consisted of 27 women and 15 men with a mean age at onset of symptoms of 52.2 ± 10.7 years (mean ± SD; range 17-72 years). Hyperprolactinemia was detected in 10 patients (24%), ranging from 16 ng/ml to 96.6 ng/ml in men (normal range 3-14.7 ng/ml) and from 31.3 ng/ml to 102.5 ng/ml in women (normal range 3.8-23.2 ng/ml). In a multivariate analysis, only brain sagging on MRI was associated with hyperprolactinemia. Brain sagging was present in 60% of patients with hyperprolactinemia and in 19% of patients with normal prolactin levels (p = 0.02). Following successful treatment of the spontaneous intracranial hypotension, hyperprolactinemia resolved, along with normalization of brain MRI findings in all 10 patients.
CONCLUSIONS: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension is a previously undescribed cause of hyperprolactinemia. Brain sagging causing distortion of the pituitary stalk (stalk effect) may be responsible for the hyperprolactinemia.
PMID: 25380110

